|
Confidence in research |
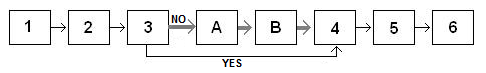
Skip a group of questions

Question 3 asks, "Have you ever been to Rome? (a) yes (b) no".
If participants select "NO" they go to Question A; those who select "YES" skip to question 4. Only participants who have traveled to Rome answer questions A and B about Rome. This approach can greatly shorten a survey for participants who do not meet the criteria you set.
Split participants into different survey groups
In Survey 1, the first question asks for participants' gender: (a) female , and (b) male. Participants who select (a) are sent to Survey 2, while those who choose (b) either continue in the current survey OR can be routed to a different survey.
Eligibility Test
To allow only certain participants to take your survey, Question 1 asks, "Have you smoked a cigarette in the last 12 months? (a) yes (b) no". If the participant answers "yes", they go on to complete the survey for smokers. If they answer "no" participants are sent to the end of the survey OR they could be sent to another survey, which contains debriefing text ONLY for non-smokers.
Informed Consent Screening
Immediately following your informed consent text, you ask, "Do you agree with these statements AND consent to voluntarily participate in this survey? (a) yes (b) no" Participants who select "yes" go on to the next question in the survey. Participants who select "no" are sent to the end of the survey OR to another survey with debriefing text for those who choose not to participate.
Question Logic and Random Assignment
When combined with survey Random Assignment (available in Survey Options), researchers can design surveys that screen for eligibility, check for informed consent, distribute participants to conditions dependent on demographic questions, and randomly assign participants to different conditions, question orders, or stimulus combinations.